Bu görüntü, Japonya Havacılık ve Uzay Araştırma Ajansı’nın Küresel Değişim Gözlem Misyonu 1. Su “SHIZUKU” uydusu tarafından sağlanan verileri kullanarak Kuzey Kutbu’ndaki kış mevsiminde deniz buzu değişimini görselleştiriyor ve bu, birkaç Dünya gözlem uydusunu işletmek için NASA liderliğindeki bir ortaklığın parçası. Aşağıdaki makaledeki videonun tamamına bakın. Kredi: NASA’nın Bilimsel Görselleştirme Stüdyosu
Arktik deniz buzu, sonbahar ve kış boyunca büyüdükten sonra 25 Şubat’ta yıllık maksimum kapsamına ulaştı. Bu yılki kış kapsamı, ABD tarafından tutulan uydu kayıtlarında en düşük 10. Ulusal Kar ve Buz Veri Merkezibiri[{” attribute=””>NASA’s Distributed Active Archive Centers.
Arctic sea ice extent peaked at 5.75 million square miles (14.88 million square kilometers) and is roughly 297,300 square miles (770,000 square kilometers) below the 1981-2010 average maximum – equivalent to missing an area of ice slightly larger than Texas and Maine combined. This maximum ties with 2015 as the third earliest on record.
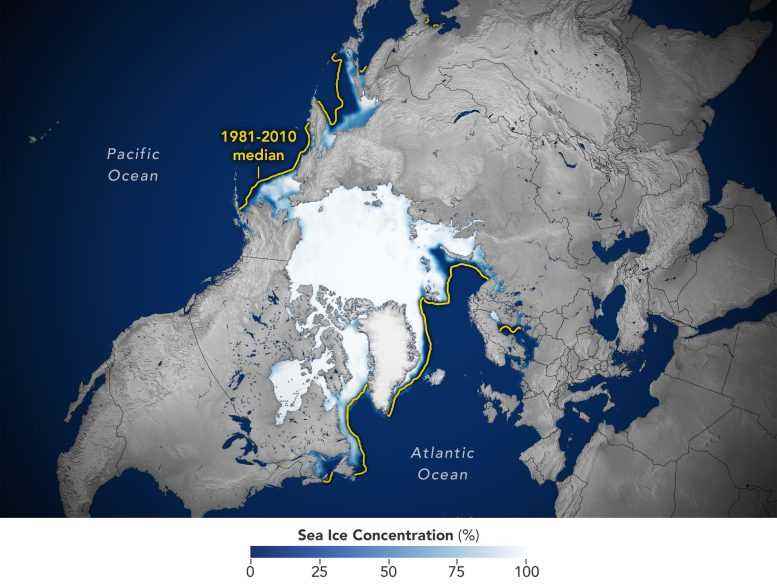
This image shows the average concentration of Arctic sea ice on February 25, 2022. The yellow outline shows the median sea ice extent for the month of March, when the ice generally reaches its maximum extent, as observed by satellites from 1981 to 2010. A median is the middle value. That is, half of the extents were larger than the line, and half were smaller. Credit: Joshua Stevens/NASA Earth Observatory
Sea ice waxes and wanes with the seasons every year. In the Arctic, it reaches its maximum extent around March after growing through the colder months, and shrinks to its minimum extent in September after melting through the warmer months. In the Southern Hemisphere, Antarctic sea ice follows an opposite cycle.
To estimate sea ice extent, satellite sensors gather sea ice data that are processed into daily images, each image grid cell spanning an area of roughly 15 miles by 15 miles (25 kilometers by 25 kilometers). Scientists then use these images to estimate the extent of the ocean where sea ice covers at least 15% of the water.
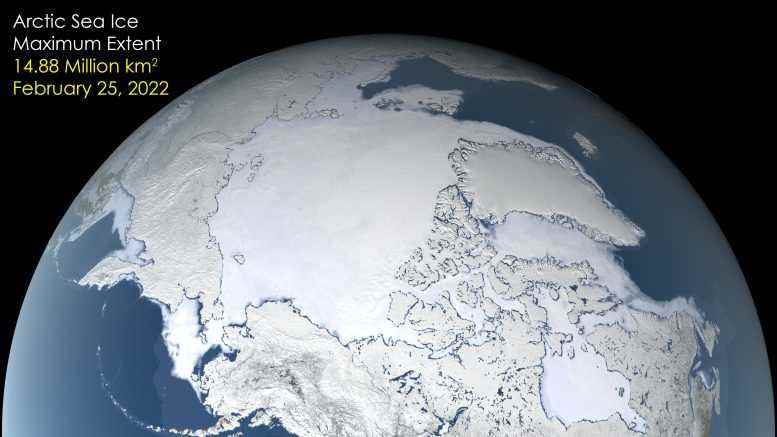

After growing through the fall and winter, sea ice in the Arctic appears to have reached its annual maximum extent. The image above shows the ice extent—defined as the total area in which the ice concentration is at least 15 percent—at its 2022 maximum, which occurred on February 25, tying with 2015 for the third earliest maximum on record. On this day the extent of the Arctic sea ice cover peaked at 14.88 million square kilometers (5.75 million square miles), making it the tenth lowest yearly maximum extent on record. Credit: NASA’s Scientific Visualization Studio
Since satellites began reliably tracking sea ice in 1979, maximum extents in the Arctic have declined at a pace of about 13% per decade, with minimum extents declining at about 2.7% per decade. These trends are linked to warming caused by human activities such as emitting carbon dioxide, which traps heat in the atmosphere and causes temperatures to rise. NASA’s analysis also shows the Arctic is warming about three times faster than other regions.
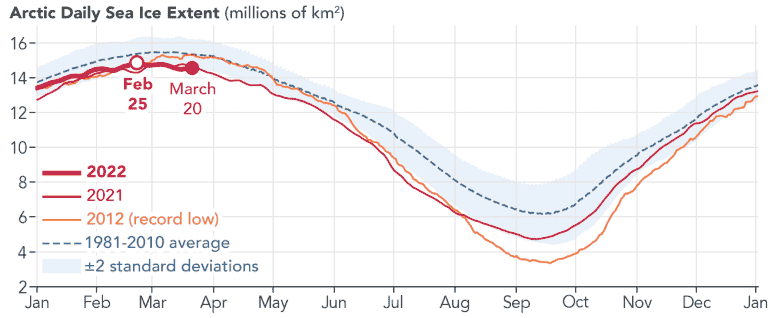
This graph shows Arctic daily sea ice extent in 2022, 2021, and 2012 compared to the 1981-2010 average. This year’s annual maximum extent was reached on February 25. Credit: Joshua Stevens/NASA Earth Observatory
This February, Antarctic sea ice dropped to a record-low minimum extent. But unlike in the Arctic, this sea ice has shown irregular ups and downs mainly because of the geographical features that surround it. Winds and ocean currents specifically linked to the Southern Ocean and Antarctica have a strong influence on sea ice extent.
Sea ice in the Arctic is surrounded by land, whereas sea ice in the Antarctic is surrounded only by ocean and can thus spread out more freely. Overall, the Antarctic sea ice record shows a slightly upward – but nearly flat – trend or increase.
Antarktika deniz buzundaki kazançlar, Kuzey Kutbu’ndaki kayıpları telafi edecek kadar büyük değil. Her iki bölgedeki buz yardımcı olur küresel sıcaklıkları düzenler. Antarktika küresel olarak dengeli deniz buzu seviyeleri kazansa bile, Arktik deniz buzu kayıpları daha fazla bölgesel ve küresel ısınmaya katkıda bulunabilir.

